| What Is Blue Light and Is it Dangerous?30 April 2020 Before the invention of artificial light, the sun was our only major source of light. Though candles lit our homes, our evenings were spent in relative darkness. Now however, our evenings are illuminated.
Blue light is environmentally friendly, and our LED lit screens are much more energy efficient than fluorescent lighting. But our bodies operate on a biological clock – the circadian rhythm – and at night extensive light can throw this off balance, and our sleep may suffer. Moreover, the latest research suggests that blue light may be linked to cancer, obesity, heart disease and diabetes. Read this blog for more information on What Is Blue Light and Is it Dangerous? What Is Blue Light?The light spectrum, cast from a single light source, is comprised of many different colour wavelengths of energy.. Not all of these colours of light have the same effect, but blue light waves are generally beneficial to our bodies as they boost:
Paradoxically, these blue light waves become the most disruptive light waves at night. In an age of electronics fitted with LED displays, and energy efficient lighting, we have increased our exposure to these blue light waves considerably. Our Circadian RhythmsEveryone has slightly different circadian rhythms but scientists have deduced that the average length of an individual's circadian rhythm to be of 24 and a quarter hours. The circadian rhythm of people who stay up late are considerably longer, whilst early birds are just short of 24 hours. Is Nighttime Exposure to Blue Light Harmful?Some recent studies have suggested that nighttime exposure to blue light waves are linked to degeneration of eyesight and peaceful sleep:
Other studies have suggested that nighttime exposure to blue light waves is linked to cancer, heart disease, diabetes and obesity. There is not definite proof that nighttime light exposure causes these, but we do know that exposure to light suppresses the secretion of melatonin. Melatonin is a hormone that influences circadian rhythms and there's some evidence that lower melatonin levels are associated with cancer. Even dim light has been found to interfere with a person's circadian rhythm and melatonin secretion. Researchers have linked short sleep to increased risk of depression, as well as diabetes and cardiovascular problems. What Effect Does Blue Light Have on Sleep?Harvard researchers conducted an experiment (the details of which can be found in the Harvard Gazette) where they compared the effects of 6.5 hours of exposure to blue light to exposure of green light of similar brightness. Blue light suppressed melatonin production twice as much as green light, and shifted circadian rhythms twice as much too. Our ConclusionIf these studies are correct in their findings, then blue light does have an unfavourable effect on our health. Moreover, these findings pose a dilemma to our search for clean energy, as LED displays and lighting (the largest emitters of blue light) are the most energy efficient light sources we have. What Can I Do To Limit Blue Light Exposure?There are several ways in which we can limit blue light exposure to lead a safer and healthier lifestyle:
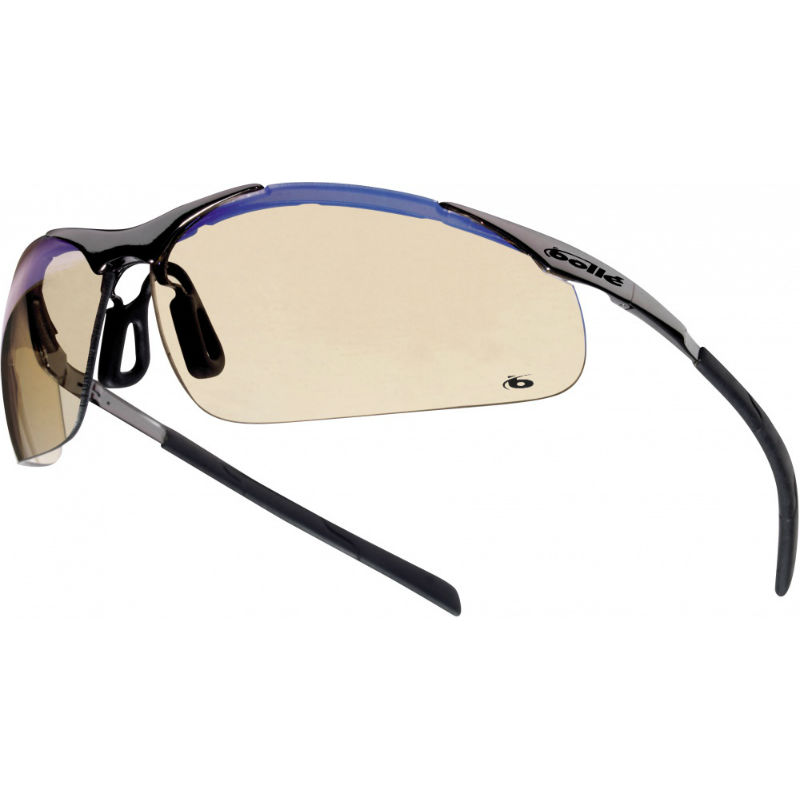
What Are Blue Light Safety Glasses?Blue light glasses are glasses with filters in their lenses that block or absorb blue light, and in some cases UV light, from getting through. That means if you use these glasses when looking at a screen, especially after dark, they can help reduce exposure to blue light waves. Our Selection of Blue Light Safety GlassesBollé Contour Metal ESP Lens Panoramic Safety Glasses CONTMESPWith an ESP lens and numerous protective properties, the Bollé Contour Metal ESP Lens Panoramic Safety Glasses CONTMESP are suited to providing eye protection in a wide range of industries, with particular benefit during tasks where risks caused by exposure to sun glare or blue light are present. The glasses are scratch resistant, lightweight and provide an enhanced field of view of 180°. The European standards to which these glasses comply are as follows: EN 166 - Personal Eye Protection JSP Continental Wraparound Blue Light Blocker Safety GlassesFeaturing blue light blocking lenses, the JSP Continental Wraparound Blue Light Blocker Safety Glasses protect the wearer from harsh blue light waves that can leave you awake post-shift for hours. These glasses are constructed to wrap around the wearer's face, increasing the firmness of which they are secured. Their soft material components are utilised around the sensitive parts of the face, ensuring maximum ease and security. The European standards to which these glasses comply are as follows: EN 166 - Personal Eye Protection Are Any Other Styles of Safety Glasses Available?We hope this blog has been informative as to the dangers of blue light exposure. If you would like to continue browsing our selection of safety glasses and find more blue-blocker lens models, please see our full range of Bollé Eyewear, or otherwise browse our full range of JSP Protective Eyewear. If you have a favourite pair of blue-blocker glasses or have any questions about our eye protection range, please leave a comment below! |
.jpg)